Dynamic Data Analysis – v5.12.01 - © KAPPA 1988-2017
Chapte
r 4 – R ate Transient Analysis (RTA)- p140/743
Where the normalized pseudo pressure and equivalent time functions are defined as:
p
p
i
i i
i
n
base
dp
z
p
p
z
pm
2
2
) (
t
t
g
g
g
ti
gi
egas
dt
pcp
t q
t q
c
t
0
) ( ) (
)(
)(
Using the equality derived from the P.S.S. equation:
)( ) (
2)(
pm pm
p
GZ
tq
c
t
i
i
i i
i
t i
a
equation (1) can be changed to give:
)(
) (
)(
t
w n
n
qb pm pm
(2)
The principle of the flowing material balance method is:
Create a plot of
)(
)(
) (
t
n
i
n
q
pm pm
versus
a
t
As the system goes into pseudo steady state flow, the points will converge towards a straight
line: the intercept at ta = 0 hrs is b.
Having b:
1.
The equation (2) is used to calculate
p
from pw, b, and q(t).
2.
Zp
/
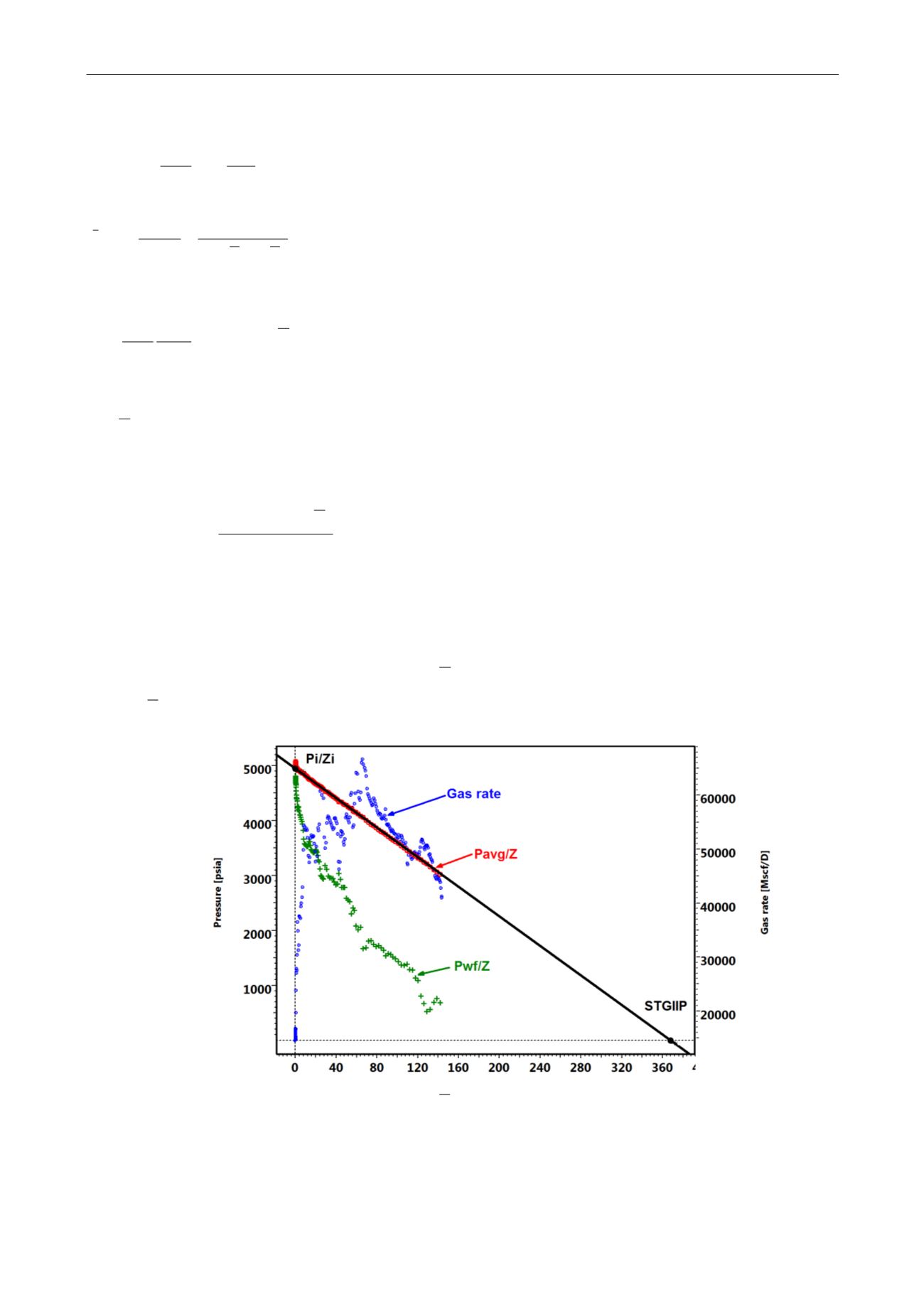
is plotted versus Q:
Fig. 4.C.9 –
Zp
/
versus Q plot
3.
A straight line is drawn through the Pavg/Z and extrapolated to get Gi.