Dynamic Data Analysis – v5.12.01 - © KAPPA 1988-2017
Chapte
r 6 – W ell models -p189/743
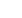
The following figure illustrates this behavior on the loglog plot.
Fig. 6.E.3 – Finite conductivity fracture behavior
6.E.4
Sensitivity to different parameters
6.E.4.a
Sensitivity to k
f
w
f
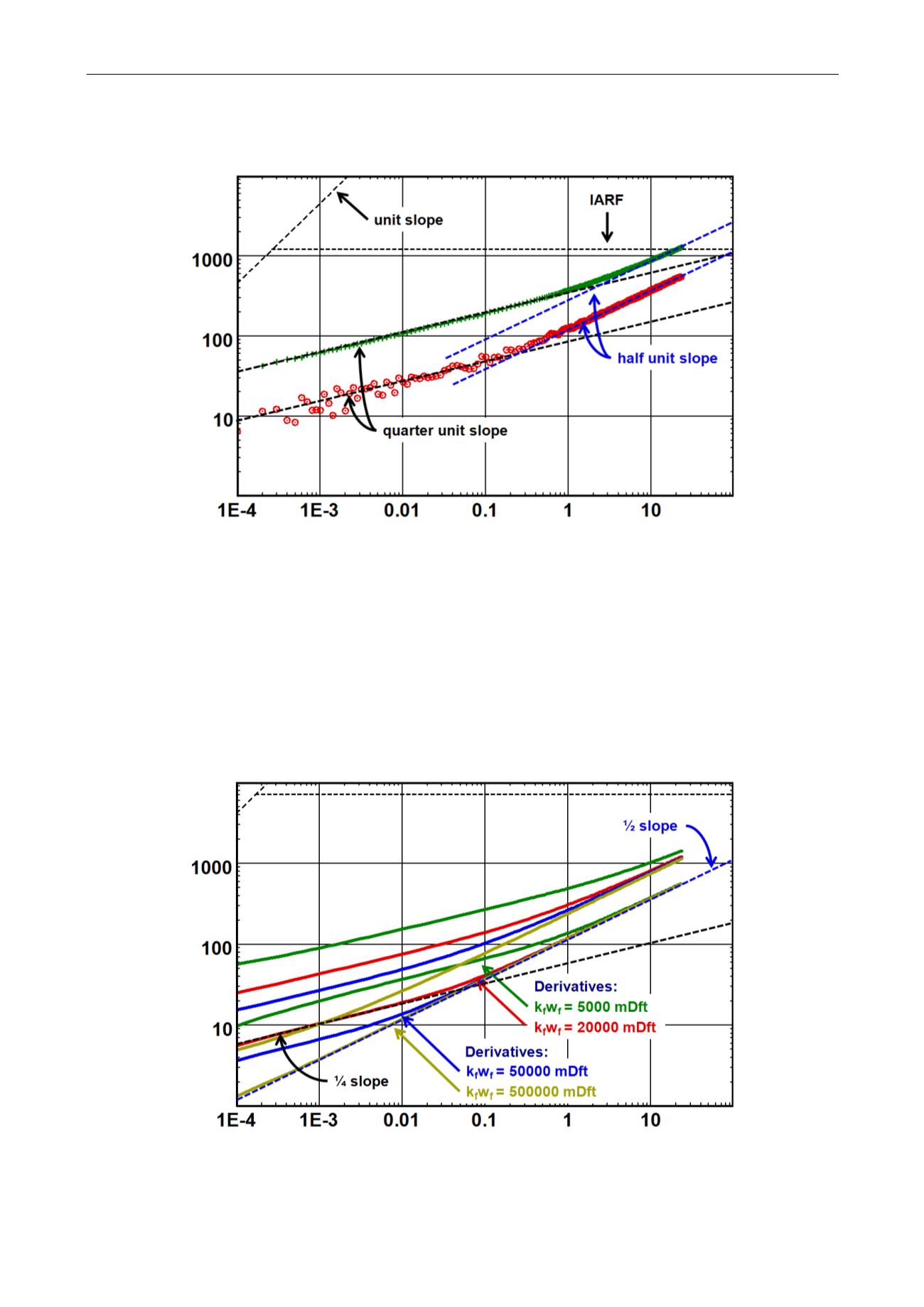
For larger fracture conductivities the solution approaches that of an infinite conductivity
fracture and the bi-linear flow will disappear completely as the derivative and the pressure
change is shifted lower and lower, the ¼ slope will be completely replaced by the linear ½
slope. See the illustration in the figure below.
Fig. 6.E.4 – Finite conductivity fracture, sensitivity to k
f
w
f
With very low fracture conductivity the linear flow will not develop and the bi-linear flow will be
dominating until the unset of infinite acting radial flow.