Dynamic Data Analysis – v5.12.01 - © KAPPA 1988-2017
Chapte
r 4 – R ate Transient Analysis (RTA)- p132/743
A match will bring values of
r
e
and
kh
,
D
i
and
q
i
. The type of decline,
b
is not linked to any of
the match ratios, obtained by selecting the correct type-curve. From the external boundary
distance, the reservoir pore volume can be calculated. From the Arps parameters, the future
performance can be forecast; N
pi
can be calculated as well as N
p
for any specified
abandonment rate.
4.B.3
Gas material balance
ZP
vs Q plot
In case of dry gas reservoir a classical method can also be applied, using the
ZP
vs Q plot.
The method assumes to get several reliable static average pressure values in the well history.
The method is based on the simple material balance equation:
gi
g
g
B B
QB
Gi
Where Gi is the gas initially in place and Q the cumulative gas production.
Estimating the Bg by:
P
TZ
B
g
00504 .0
The equation becomes:
i
i
i
i
Z
P
Q
GZ
P
Z
P
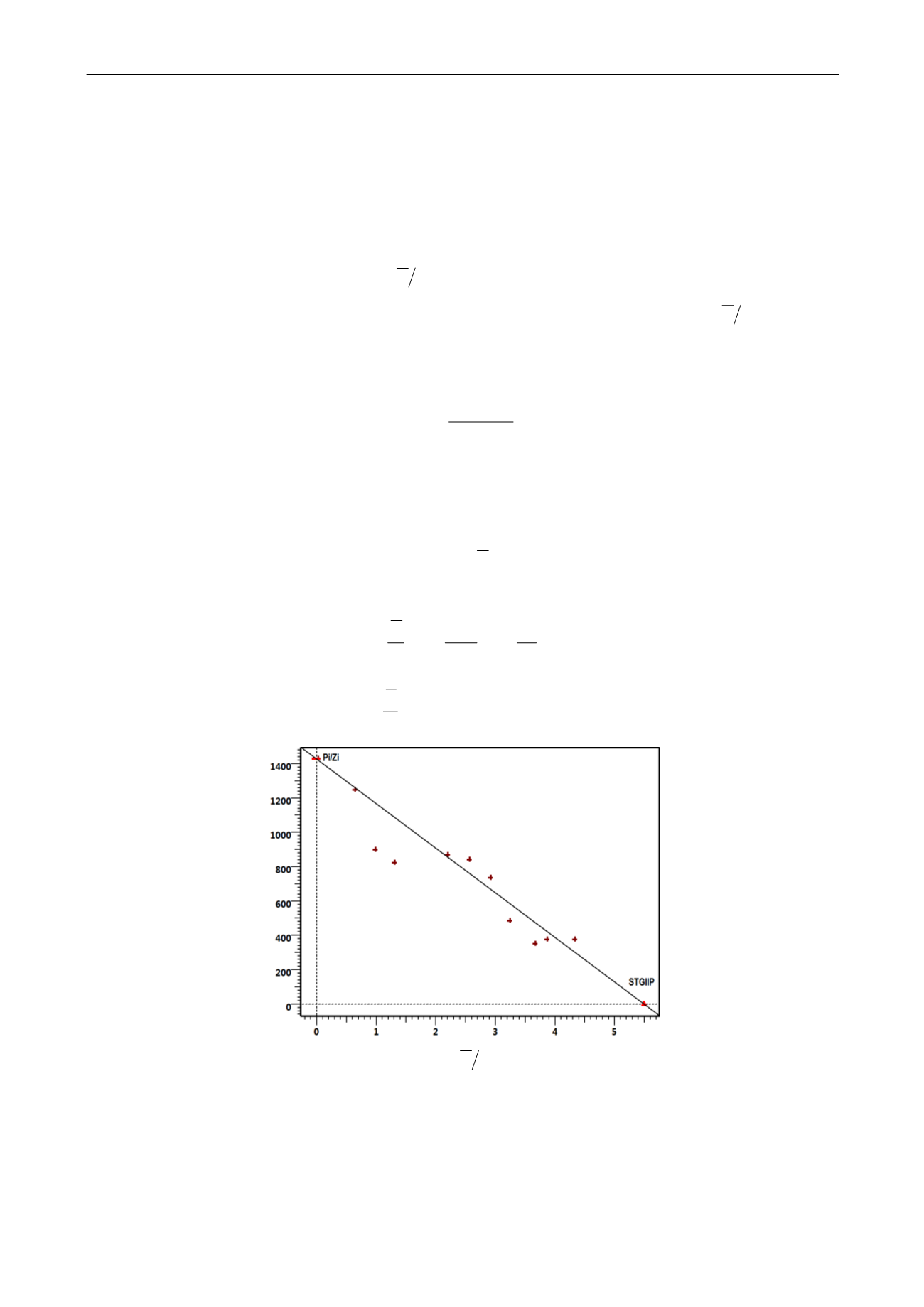
This equation indicates that a plot of
Z
P
versus Q extrapolates to the gas initially in place Gi.
Fig. 4.B.4
–
ZP
vs Q plot
The validity and the accuracy of this method depend directly on the validity of the static
pressure and of the PVT parameters.