Dynamic Data Analysis – v5.12.01 - © KAPPA 1988-2017
Chapte
r 4 – R ate Transient Analysis (RTA)- p153/743
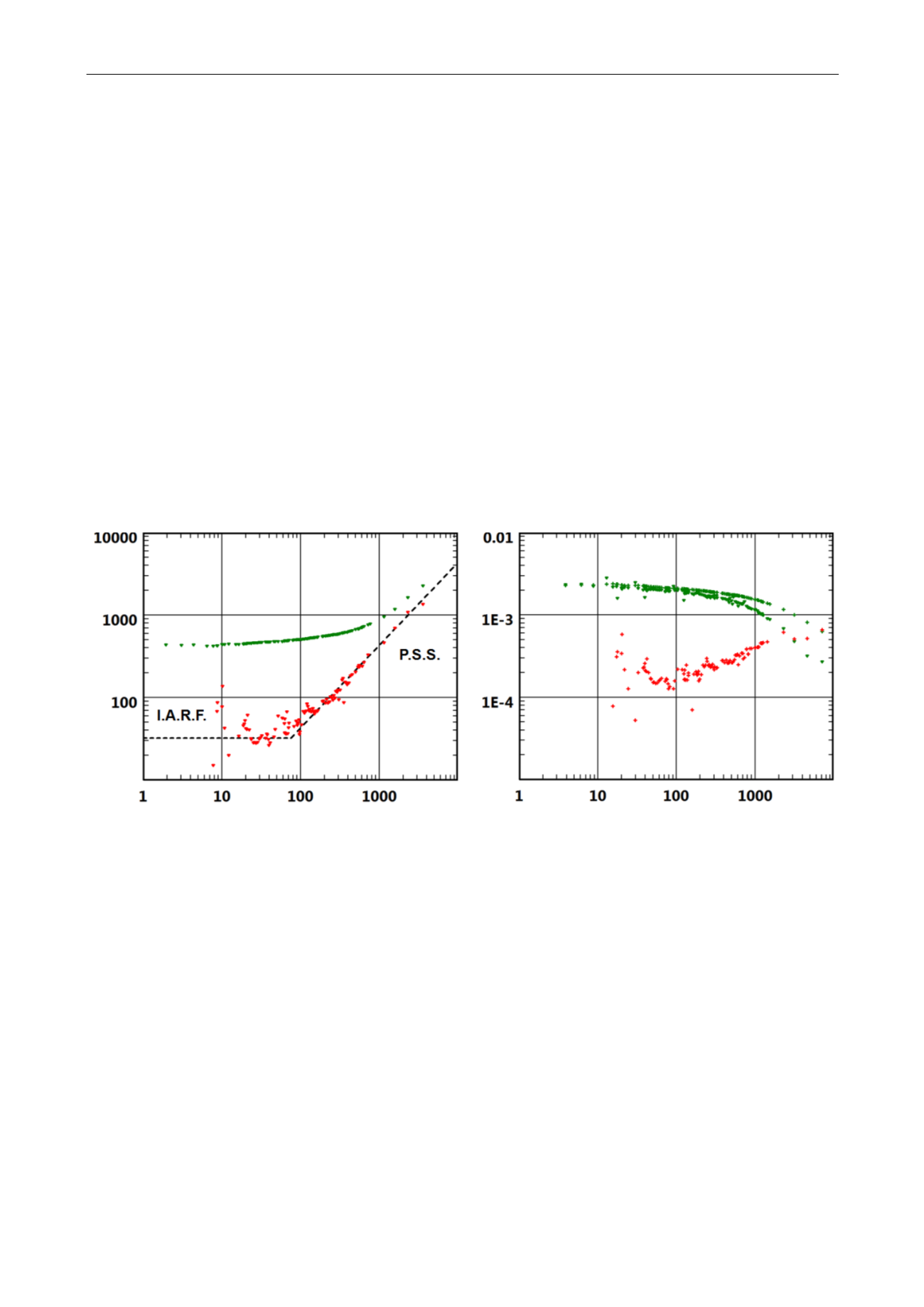
The loglog plot (see below) is used for diagnostic purposes to identify the two main flow
regimes hopefully present in production data, infinite acting radial flow (IARF) and pseudo
steady state (PSS). The pressure match is fixed to coincide with a stabilization of the
derivative of the normalized pressure integral and the time match is fixed to the unit slope line
of PSS at late time. The pressure match and the time match are adjusted by click and drag of
the mouse. The loglog plot is linked to the Blasingame and the Fetkovich plot so any change in
the loglog match is mirrored in the others. In case the data is of high quality and the sampling
frequency is high enough it is sometimes possible that more than the IARF transient develop
thus extending the diagnostic possibilities to approach those of PTA and both well and
reservoir models can be recognized in the test data. This is however rare in low frequency data
typically used in rate transient analysis.
If the loaded pressure history contains any decent build-ups with high frequency pressure data
or a link to a database that allows the repopulation of this data without a filter then the
interpreter is in luck. This data can be transferred to a PTA module to determine all of the
classical parameters including the model and these can be transferred back to the RTA
package and finally the modelling can begin; adjusting for parameters that can typically
change over the longer time intervals involved in rate transient analysis (i.e. skin).
Fig. 4.E.1 – Match on the Loglog plot
Fig. 4.E.2 – Blasingame plot
4.E.4
Model generation
After the diagnostics candidate models, analytical or numerical, are selected and an attempt is
made to obtain a match between the models and the real data in all the relevant plots
including the history plot. To obtain a match the interpreter will run with a first estimate of the
model parameters generally obtained by generating the default, or automatic, model based on
the initial match made in the loglog plot as described in the previous section. The default
model is the homogenous model with constant skin in a closed circle. At generation time a first
estimate of the constant skin is automatically made by the software.
After a comparison between the model and the data, changes can be made to the model
parameters and any known well configuration can be imposed such as knowledge of the well
being fractured, horizontal or partially penetrating. In the event that PTA was performed on
part of the pressure data the model used can be transferred to the rate transient analysis.
Finally the objective is to vary the model parameters until there is a reasonable match
between the model and the data in all relevant plots, including the history plot.